Understanding DRAM: A Crucial Component in Computing
Dynamic Random-Access Memory, commonly known as DRAM, is a key component in modern computing systems. It is a type of volatile memory that stores data and machine code that the CPU needs to access quickly for ongoing operations. Unlike non-volatile memory such as hard drives or SSDs, DRAM requires power to retain data, making it faster but temporary.
DRAM is used in a wide range of devices, from personal computers to mobile phones and servers. Its high-speed nature makes it ideal for storing data that needs to be accessed quickly and frequently during system operation. When you open an application on your computer or load a webpage on your phone, DRAM plays a crucial role in providing the necessary data to the CPU for processing.
One of the key characteristics of DRAM is its dynamic nature. This means that data stored in DRAM needs to be constantly refreshed to maintain its integrity. If power is lost or interrupted, the data stored in DRAM will be lost. This is why computers and other devices need to save important data to non-volatile storage devices like hard drives or SSDs.
DRAM comes in various form factors and speeds, with newer generations offering higher capacities and faster access times. As technology advances, manufacturers continue to improve DRAM modules to meet the increasing demands of modern computing applications.
In conclusion, DRAM is an essential component in computing systems that provides fast and temporary storage for data that needs to be accessed quickly by the CPU. Its dynamic nature and high-speed capabilities make it indispensable for a wide range of devices and applications.
Understanding DRAM: Key Questions Answered
- What is DRAM and how does it differ from other types of memory?
- Why is DRAM considered volatile memory?
- How does DRAM work in computing systems?
- What are the common uses of DRAM in electronic devices?
- What factors should be considered when choosing DRAM for a computer or device?
What is DRAM and how does it differ from other types of memory?
Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DRAM) is a type of volatile memory commonly used in computing systems to store data that the CPU needs quick access to during ongoing operations. Unlike non-volatile memory such as hard drives or SSDs, DRAM requires power to retain data, making it faster but temporary. DRAM differs from other types of memory in its speed and volatility, as it provides fast access to data but loses that data when power is removed. This dynamic nature of DRAM makes it ideal for storing data that needs to be accessed quickly and frequently during system operation, distinguishing it from non-volatile memory options that retain data even when power is turned off.
Why is DRAM considered volatile memory?
DRAM is considered volatile memory due to its characteristic of requiring power to retain stored data. Unlike non-volatile memory such as hard drives or SSDs, DRAM does not retain data when the power is turned off or interrupted. This volatile nature of DRAM makes it ideal for storing data that needs to be accessed quickly during ongoing operations but necessitates a backup mechanism to prevent data loss in case of power failure.
How does DRAM work in computing systems?
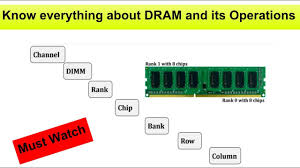
Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DRAM) works in computing systems by storing data and machine code that the CPU needs to access quickly for ongoing operations. When a program or application is running, the CPU sends requests to retrieve data stored in DRAM. DRAM stores this data in cells organized in rows and columns, with each cell holding a single bit of information. To access specific data, the CPU sends row and column addresses to the DRAM module, allowing it to locate and retrieve the required information quickly. DRAM operates at high speeds, making it ideal for storing and accessing data that needs to be processed rapidly during system operation.
What are the common uses of DRAM in electronic devices?
Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DRAM) is widely used in electronic devices for various purposes. One common use of DRAM is as the main system memory in computers, laptops, and servers. It serves as temporary storage for data and program instructions that the CPU needs to access quickly during operation. Additionally, DRAM is commonly found in smartphones and tablets to support multitasking capabilities and ensure smooth performance when running multiple apps simultaneously. Another common use of DRAM is in networking equipment such as routers and switches, where it helps in buffering and processing data packets efficiently. Overall, DRAM plays a crucial role in enhancing the speed and responsiveness of electronic devices across different applications and industries.
What factors should be considered when choosing DRAM for a computer or device?
When choosing DRAM for a computer or device, several factors should be taken into consideration to ensure optimal performance and compatibility. First and foremost, the compatibility of the DRAM with the specific system or device is crucial. This includes checking for the correct type, speed, and capacity of DRAM that is supported by the motherboard or device. Additionally, considering the intended use of the computer or device is important, as different applications may require varying amounts of memory. Factors such as budget constraints, brand reputation, and warranty coverage should also be considered when selecting DRAM to ensure a reliable and cost-effective choice for enhancing system performance.
Tags: computing systems, data access, data loss prevention, dram, dynamic nature, fast access, non-volatile memory, ongoing operations, power, temporary storage, volatile memory, what is dram