NAND and NOR Flash: Understanding the Basics of Flash Memory
Flash memory has become an integral part of our digital lives, powering everything from smartphones and tablets to solid-state drives (SSDs) and USB drives. Among the various types of flash memory, NAND and NOR are the most widely used. Let’s delve into what sets them apart and how they contribute to our everyday technology.
NAND Flash:
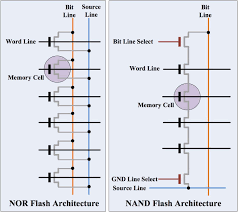
NAND flash memory is the more common type, known for its high storage capacity and cost-effectiveness. It is commonly found in USB drives, memory cards, and SSDs. NAND (Not AND) gets its name from the logic gate it employs to store data. It uses a series of transistors connected in a grid-like structure to store information in a binary format.
One key advantage of NAND flash is its ability to store multiple bits of data per cell, known as multi-level cell (MLC) or triple-level cell (TLC) technology. This allows for higher storage densities at a lower cost per gigabyte compared to NOR flash.
However, NAND flash has some limitations. It has slower read and write speeds compared to NOR flash due to its architecture. Additionally, it requires an erase-before-write operation, meaning data must be erased before new information can be written onto it.
NOR Flash:
NOR flash memory is less common but offers certain advantages over NAND flash. Its architecture is based on NOR gates, which allow for random access read capabilities similar to traditional computer RAM. This makes it suitable for applications that require fast read times or execute code directly from the memory.
NOR flash is commonly used in devices like microcontrollers, embedded systems, and firmware applications where quick access to specific data or program instructions is crucial.
Unlike NAND flash, NOR flash does not require an erase-before-write operation as it supports byte-level random access writes. This makes it easier to modify individual bits or bytes of data without the need to erase and rewrite entire blocks.
However, NOR flash has a higher cost per gigabyte compared to NAND flash due to its lower storage density. It is typically used for smaller capacity applications where speed and random access are prioritized over cost-efficiency.
Conclusion:
NAND and NOR flash memory serve different purposes in our digital landscape. NAND flash offers high storage capacity at a lower cost per gigabyte, making it ideal for devices that require large amounts of data storage. On the other hand, NOR flash provides faster random access read capabilities, making it suitable for applications that require quick retrieval of specific data or program instructions.
Understanding the differences between NAND and NOR flash can help us make informed decisions when choosing devices that rely on flash memory. Whether it’s a USB drive, an SSD, or an embedded system, both types of flash memory play vital roles in powering our modern technology.
Frequently Asked Questions About NAND and NOR Flash: Speed Comparison, Purpose, and SD Card Classification
- Why is NAND flash faster than NOR flash?
- What is the purpose of NOR flash?
- What is NAND and NOR flash?
- Is SD card is NAND or NOR flash?
Why is NAND flash faster than NOR flash?
NAND flash is generally faster than NOR flash due to differences in their underlying architectures and access methods.
NAND flash memory is organized in a grid-like structure, with multiple memory cells connected in series. This architecture allows for high storage density but results in slower read and write speeds. When reading data from NAND flash, the entire row of memory cells needs to be accessed, which takes time. Similarly, when writing data, the entire block needs to be erased before new information can be written. This sequential nature of accessing data contributes to the relatively slower speed of NAND flash.
On the other hand, NOR flash memory has a different architecture that allows for random access read capabilities similar to traditional computer RAM. It uses NOR gates to connect individual memory cells, enabling direct access to specific locations within the memory array. This random access feature makes NOR flash faster when it comes to retrieving specific data or executing code directly from the memory.
However, it’s important to note that while NAND flash is generally slower in terms of read and write speeds compared to NOR flash, it excels in terms of storage capacity and cost-effectiveness. NAND flash’s ability to store multiple bits per cell (MLC or TLC technology) allows for higher storage densities at a lower cost per gigabyte compared to NOR flash.
In summary, NAND flash’s sequential access method contributes to its slower speed compared to NOR flash’s random access capability. However, both types of flash memory have their own advantages and are used in different applications based on specific requirements such as speed, storage capacity, and cost considerations.
What is the purpose of NOR flash?
The purpose of NOR flash is to provide fast random access read capabilities, making it suitable for applications that require quick retrieval of specific data or program instructions. Unlike NAND flash, NOR flash allows for byte-level random access writes, which means individual bits or bytes of data can be modified without the need to erase and rewrite entire blocks.
NOR flash memory is commonly used in devices such as microcontrollers, embedded systems, and firmware applications. These devices often require quick access to specific data or execute code directly from the memory. The random access capability of NOR flash allows for efficient execution of code and faster retrieval of critical information.
Due to its architecture and faster read times, NOR flash is well-suited for applications where speed and direct access are prioritized over cost-efficiency or high storage capacity. Examples include boot loaders, BIOS (Basic Input/Output System), firmware storage in networking equipment, and other systems that require fast and reliable access to stored data.
In summary, the purpose of NOR flash is to provide fast random access read capabilities, enabling efficient execution of code and quick retrieval of specific data in applications where speed and direct access are crucial.
What is NAND and NOR flash?
NAND and NOR flash are two types of non-volatile memory technologies commonly used in electronic devices. They are both forms of flash memory, which means they can retain data even when power is removed.
NAND Flash:
NAND flash memory is a type of solid-state storage that offers high capacity and cost-effectiveness. It is widely used in devices such as USB drives, memory cards, SSDs, and smartphones. NAND (Not AND) gets its name from the logic gate it uses to store data. It employs a grid-like structure of transistors to store information in a binary format.
One significant advantage of NAND flash is its ability to store multiple bits of data per cell, known as multi-level cell (MLC) or triple-level cell (TLC) technology. This allows for higher storage densities at a lower cost per gigabyte compared to other memory technologies.
However, NAND flash has some limitations. It has slower read and write speeds compared to other types of memory due to its architecture. Additionally, it requires an erase-before-write operation, meaning data must be erased before new information can be written onto it.
NOR Flash:
NOR flash memory is another type of non-volatile storage technology used in various applications such as microcontrollers, embedded systems, and firmware applications. Unlike NAND flash, NOR flash uses NOR gates for storing and retrieving data. This architecture allows for random access read capabilities similar to traditional computer RAM.
One key advantage of NOR flash is its ability to execute code directly from the memory itself. This makes it suitable for applications that require fast access to specific data or program instructions.
Unlike NAND flash, NOR flash does not require an erase-before-write operation as it supports byte-level random access writes. This makes it easier to modify individual bits or bytes of data without the need to erase and rewrite entire blocks.
However, NOR flash typically has lower storage density compared to NAND flash, resulting in higher cost per gigabyte. It is commonly used for applications that prioritize speed and random access over cost-efficiency.
In summary, NAND and NOR flash are two different types of flash memory technologies. NAND flash offers high capacity and cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for devices that require large amounts of data storage. NOR flash provides faster random access read capabilities, making it ideal for applications that need quick retrieval of specific data or program instructions.
Is SD card is NAND or NOR flash?
SD cards typically use NAND flash memory. NAND flash offers higher storage capacity and cost-effectiveness, making it a suitable choice for SD cards that require ample storage space. The architecture of NAND flash allows for efficient data storage in a compact form factor, making it ideal for portable memory solutions like SD cards.
Tags: architecture, basics, binary format, byte-level random access writes, computer ram, cost-effectiveness, digital landscape, embedded systems, erase-before-write operation, firmware applications, flash memory, grid-like structure, high storage capacity, logic gate, memory cards, microcontrollers, multi-level cell mlc, nand flash, nand nor flash, nor flash, random access, random access read capabilities, read and write speeds, smartphones, solid-state drives ssds, ssds, storage densities, storage density, tablets, transistors, triple-level cell tlc technology, types of flash memory, usb drives