NAND Flash: Revolutionizing Data Storage
In today’s digital age, data storage plays a crucial role in our everyday lives. From smartphones and laptops to cameras and gaming consoles, we rely on storage solutions that are not only fast and reliable but also compact and energy-efficient. One technology that has revolutionized the way we store data is NAND Flash.
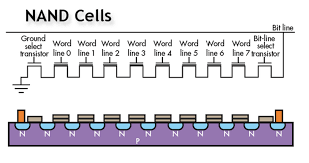
NAND Flash memory, commonly referred to as just NAND, is a type of non-volatile storage technology that has become the backbone of modern data storage devices. It is widely used in USB drives, solid-state drives (SSDs), memory cards, and even in some mobile devices.
So, what makes NAND Flash so special? Let’s dive deeper into its key features and benefits.
Firstly, NAND Flash offers high-density storage capabilities. This means it can store a large amount of data in a relatively small physical space. As a result, devices like smartphones and tablets can have ample storage capacity without sacrificing their sleek designs.
Secondly, NAND Flash provides fast read and write speeds. Compared to traditional hard disk drives (HDDs), which rely on spinning magnetic disks, NAND-based SSDs offer significantly faster access times. This translates into quicker boot-up times for computers, faster file transfers for users, and smoother overall performance.
Furthermore, NAND Flash memory offers excellent durability and reliability. Unlike HDDs with moving parts that are prone to mechanical failures, NAND-based devices have no moving parts. This makes them more resistant to shock, vibration, and temperature variations. Additionally, NAND Flash can withstand a higher number of program/erase cycles before wearing out.
Energy efficiency is another advantage of NAND Flash technology. Due to its solid-state nature, it consumes less power compared to traditional storage solutions. This not only prolongs battery life in portable devices but also reduces energy consumption in data centers where large-scale SSD deployments are becoming increasingly common.
It’s worth noting that there are different types of NAND Flash, including Single-Level Cell (SLC), Multi-Level Cell (MLC), and Triple-Level Cell (TLC). Each type offers a different balance between performance, endurance, and cost. SLC provides the highest endurance and fastest performance but at a higher cost, while TLC offers higher capacity at a lower cost but with slightly lower endurance.
As NAND Flash technology continues to evolve, manufacturers are constantly pushing the boundaries of what is possible. We have seen advancements such as 3D NAND, which stacks memory cells vertically to increase storage density even further. This allows for more data to be stored in the same physical footprint.
In conclusion, NAND Flash has transformed the way we store and access data. Its high-density storage capabilities, fast read/write speeds, durability, energy efficiency, and ongoing technological advancements make it an indispensable component of modern storage devices. As our reliance on digital data continues to grow, NAND Flash will undoubtedly play a critical role in shaping the future of data storage technology.
7 Advantages of NAND Flash: Unleashing High-Speed Performance, Low Power Consumption, Durability, Compact Size, Cost Effectiveness, Flexibility, and Scalability
- High-speed performance
- Low power consumption
- Durability
- Compact size
- Cost effectiveness
- Flexibility
- Scalability
Drawbacks of NAND Flash: High Cost, Limited Write Cycles, Low Data Transfer Rates, and Vulnerability to Power Loss
High-speed performance
High-speed Performance: Unleashing the Power of NAND Flash
In today’s fast-paced digital world, speed is everything. Whether it’s loading applications, transferring files, or accessing data, we want things to happen in an instant. This is where NAND flash memory comes into play, offering a significant advantage over traditional hard drives with its high-speed performance.
NAND flash technology has revolutionized the way we store and access data. Unlike traditional hard drives that rely on spinning disks and mechanical components, NAND flash memory utilizes solid-state storage, resulting in lightning-fast read and write speeds. This makes it a perfect choice for applications that demand rapid data access and high-performance computing.
One of the key benefits of NAND flash is its ability to deliver faster read/write speeds compared to traditional hard drives. When you click on a file or launch an application stored on a NAND-based storage device, it responds almost instantly. This near-instantaneous response time enhances user experience by reducing waiting times and boosting overall system performance.
The high-speed performance of NAND flash is particularly advantageous in various scenarios. For example, in professional environments where large amounts of data need to be processed quickly, such as video editing or 3D rendering, NAND-based storage solutions can significantly reduce processing times and enhance productivity.
Furthermore, gamers can benefit from the high-speed performance of NAND flash when it comes to loading game levels or accessing game assets. With faster read speeds offered by SSDs powered by NAND flash memory, gamers can enjoy reduced loading times and seamless gameplay experiences without interruptions.
Moreover, businesses that rely on real-time analytics or database management systems can leverage the speed advantage of NAND flash memory. The ability to quickly retrieve and process data enables faster decision-making processes and enhances overall operational efficiency.
It’s important to note that the high-speed performance of NAND flash doesn’t just benefit power users or professionals; it also improves everyday tasks for regular users. From booting up your computer in seconds to quickly transferring large files or multitasking seamlessly, NAND flash memory enhances the overall user experience by delivering swift and responsive performance.
In conclusion, the high-speed performance of NAND flash is a game-changer in the world of data storage. Its ability to offer faster read/write speeds compared to traditional hard drives opens up new possibilities for high-performance computing applications. Whether it’s for professional use, gaming, or everyday tasks, NAND flash memory empowers users with quick and efficient data access, ensuring that we can keep up with the speed of our digital lives.
Low power consumption
NAND Flash: Empowering Mobile Devices with Low Power Consumption
In the fast-paced world of mobile devices, one crucial factor that users prioritize is battery life. The longer a device can operate without needing a recharge, the more convenient it becomes for users on the go. This is where NAND Flash memory technology shines with its low power consumption, offering significant advantages over traditional hard disk drives (HDDs).
NAND Flash consumes considerably less energy than HDDs, making it an ideal choice for mobile devices such as smartphones, tablets, and portable media players. By utilizing NAND-based storage solutions, manufacturers can optimize power efficiency and extend battery life.
The low power consumption of NAND Flash has a direct impact on the overall performance and usability of mobile devices. With reduced energy requirements, these devices can operate for more extended periods without draining their batteries quickly. This means users can enjoy uninterrupted usage throughout the day without worrying about running out of power at critical moments.
Furthermore, NAND Flash’s low power consumption not only benefits battery life but also contributes to a more eco-friendly approach to technology. By reducing energy consumption in mobile devices, we are indirectly minimizing our carbon footprint and conserving valuable resources.
Another advantage of NAND Flash’s low power consumption is its impact on heat generation. Compared to HDDs that generate considerable heat due to mechanical components, NAND-based storage generates significantly less heat during operation. This reduction in heat dissipation helps maintain optimal operating temperatures within mobile devices, contributing to their overall longevity and reliability.
Moreover, the efficiency gained from low power consumption allows manufacturers to design sleeker and lighter mobile devices. With less energy needed for storage operations, there is more room for other components or larger batteries within the device’s limited space. This enables manufacturers to create slim and lightweight products without compromising on functionality or performance.
As technology continues to advance at a rapid pace, NAND Flash’s low power consumption remains a crucial advantage for mobile device users worldwide. It not only enhances battery life but also contributes to a more sustainable and efficient approach to technology usage. With NAND-based storage solutions, we can expect our mobile devices to become even more power-efficient in the future, enabling us to stay connected and productive for longer periods without the constant need for recharging.
Durability
Durability: The Reliable Advantage of NAND Flash
In the world of data storage, durability is a key factor that users value. This is where NAND flash memory truly shines. Unlike traditional hard drives that rely on mechanical components, NAND flash is not subject to the same wear and tear. This makes it an incredibly reliable option over time.
The absence of moving parts in NAND flash memory is a game-changer. Hard drives consist of spinning disks and read/write heads that are susceptible to mechanical failures. On the other hand, NAND flash memory utilizes a solid-state design, which means it has no moving parts whatsoever.
This inherent durability offers several advantages. First and foremost, it makes NAND flash significantly more resistant to physical shocks and vibrations. Whether you accidentally drop your device or experience sudden jolts during transportation, NAND flash can withstand these impacts without compromising your data.
Furthermore, the absence of mechanical components in NAND flash eliminates the risk of disk failure due to wear and tear over time. Hard drives have limited lifespans as their moving parts gradually wear out. In contrast, NAND flash memory can endure a higher number of program/erase cycles before wearing out.
This increased durability translates into enhanced reliability for users. You can trust that your data will remain intact and accessible for longer periods with NAND flash-based storage solutions. Whether you are using a USB drive or an SSD in your computer, the solid-state nature of NAND flash ensures that your files are safe from mechanical failures.
Additionally, the durability of NAND flash extends its usefulness in various environments. It can withstand extreme temperatures better than traditional hard drives since there are no sensitive moving parts affected by heat or cold. This makes it ideal for applications where temperature variations are common, such as industrial settings or outdoor use.
In summary, the durability offered by NAND flash memory sets it apart from traditional hard drives. Its solid-state design eliminates the vulnerabilities associated with mechanical components, making it highly reliable over time. With NAND flash, you can have peace of mind knowing that your data is protected from physical shocks, vibrations, and the wear and tear that comes with mechanical parts. Embrace the durability of NAND flash and enjoy a more reliable data storage experience.
Compact size
NAND Flash: The Perfect Fit for Mobile Devices
When it comes to mobile devices like smartphones and tablets, every ounce of space matters. That’s where NAND Flash memory comes in as a game-changer. One of its standout advantages is its compact size, which makes it an ideal storage solution for these portable gadgets.
Compared to traditional hard disk drives (HDDs), NAND Flash is significantly smaller and lighter in weight. This compactness allows manufacturers to design sleek and slim devices without compromising on storage capacity. With NAND Flash, mobile devices can offer ample storage space while maintaining their slim profiles.
The small size of NAND Flash also brings other practical benefits. It enables manufacturers to maximize internal space utilization, allowing for the inclusion of other essential components such as larger batteries or advanced processors. This translates into longer battery life and improved overall performance, enhancing the user experience.
Moreover, the lightweight nature of NAND Flash contributes to the portability and ease of use of mobile devices. Carrying a smartphone or tablet that weighs less not only feels more comfortable but also adds convenience for users on the go.
Additionally, the compact size of NAND Flash has opened up new possibilities in terms of device form factors. It has paved the way for wearable technology like smartwatches and fitness trackers, where miniaturization is crucial. These small yet powerful devices rely on NAND Flash to provide sufficient storage capacity while maintaining their sleek and lightweight designs.
In summary, the compact size of NAND Flash memory has made it an indispensable component in mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets. Its small footprint allows for efficient use of internal space, resulting in slimmer designs without compromising on storage capacity. With NAND Flash, manufacturers can create portable gadgets that are both functional and aesthetically pleasing, enhancing the user experience in our increasingly connected world.
Cost effectiveness
Cost Effectiveness: The Affordable Solution of NAND Flash
When it comes to data storage solutions, cost is often a significant factor to consider. In this regard, NAND Flash technology has a clear advantage: its cost effectiveness. The cost per gigabyte of storage on a NAND flash device is lower than that of a traditional hard drive, making it an economical choice for individuals and businesses alike.
One of the reasons behind the cost effectiveness of NAND Flash is its high-density storage capabilities. NAND Flash memory can store a large amount of data in a compact physical space. This means that manufacturers can produce higher-capacity storage devices without significantly increasing production costs. As a result, consumers can enjoy more storage space at a lower price point.
Another factor contributing to the cost effectiveness of NAND Flash is its solid-state nature. Unlike traditional hard drives with moving parts and complex mechanical systems, NAND-based devices have no such components. This simplifies the manufacturing process and reduces production costs. Additionally, the absence of moving parts also leads to lower maintenance costs as there are fewer chances for mechanical failures.
Furthermore, due to its durability and reliability, NAND Flash requires less frequent replacement or repairs compared to traditional hard drives. This translates into reduced long-term costs for users and businesses alike. With longer lifespan and higher endurance levels, NAND-based devices offer excellent value for money.
Additionally, the energy efficiency of NAND Flash contributes to its overall cost effectiveness. Solid-state drives based on NAND technology consume less power compared to traditional hard drives. This not only reduces energy consumption but also lowers electricity bills in the long run.
The affordability of NAND Flash has made it increasingly popular in various applications such as consumer electronics, enterprise storage systems, cloud computing infrastructure, and more. From personal computers and laptops to data centers housing massive amounts of information, many have recognized the financial benefits that come with implementing NAND-based storage solutions.
In conclusion, the cost effectiveness of NAND Flash makes it an attractive choice for data storage solutions. Its high-density storage capabilities, solid-state nature, durability, and energy efficiency contribute to its affordability. As technology continues to advance, we can expect NAND Flash to become even more cost effective, offering greater value for our storage needs.
Flexibility
NAND Flash: The Power of Flexibility
When it comes to data storage, flexibility is key. That’s where NAND Flash memory comes into play. With its small form factor and low power consumption, NAND Flash offers a level of adaptability that makes it suitable for a wide range of devices.
One major advantage of NAND Flash is its compact size. Its small form factor allows it to be integrated into devices with limited space requirements, such as laptops, tablets, and smartphones. These portable devices demand storage solutions that can fit seamlessly within their sleek designs without compromising performance or functionality. NAND Flash delivers on this front, enabling manufacturers to create slim and lightweight devices while still providing ample storage capacity.
Moreover, NAND Flash’s low power consumption makes it an ideal choice for battery-powered devices. Laptops, tablets, and smartphones rely on energy-efficient components to maximize battery life. By using NAND Flash memory, these devices can store data without draining the battery excessively. This ensures longer usage times between charges and enhances the overall user experience.
But the flexibility of NAND Flash doesn’t stop there. It extends beyond consumer electronics into industrial equipment and embedded systems as well. In industries like manufacturing or automation, where space constraints are common, NAND Flash can be seamlessly integrated into compact systems without compromising performance or reliability. Additionally, its low power consumption makes it suitable for embedded systems powered by batteries or other limited energy sources.
The versatility of NAND Flash enables it to cater to a wide range of applications across various industries. From consumer electronics to industrial equipment and everything in between, NAND Flash proves itself as a reliable storage solution that can meet diverse needs.
In conclusion, the flexibility offered by NAND Flash is truly remarkable. Its small form factor allows for integration into devices with limited space requirements while its low power consumption ensures optimal energy efficiency in battery-powered devices. Whether it’s a laptop, tablet, smartphone, or industrial equipment with specific space or power constraints – NAND Flash provides the storage solution needed to keep these devices running smoothly. With its adaptability, NAND Flash continues to shape the landscape of modern data storage technology.
Scalability
Scalability: Unlocking Limitless Storage Potential with NAND Flash
In the ever-expanding digital landscape, businesses and individuals alike are constantly seeking ways to accommodate their growing storage needs. This is where NAND Flash technology truly shines with its remarkable scalability, allowing companies to effortlessly expand their storage capacity.
Traditionally, scaling up storage meant replacing existing hardware components or reconfiguring the entire architecture. However, NAND Flash breaks free from these limitations. Companies can easily add additional NAND Flash modules to their existing systems without the need for extensive hardware changes or disrupting their operations.
This scalability feature of NAND Flash offers unparalleled flexibility and cost-effectiveness. As data requirements increase, organizations can seamlessly integrate more NAND Flash modules into their infrastructure, expanding storage capacity on-demand. This means that businesses no longer need to invest in entirely new systems or endure costly and time-consuming migrations.
The ability to scale up with NAND Flash also ensures future-proofing of storage solutions. As technology advances and data volumes continue to surge, companies can adapt by simply adding more NAND Flash modules as needed. This agility allows organizations to stay ahead in an ever-evolving digital world without being constrained by fixed storage capacities.
Moreover, the scalability of NAND Flash has a direct impact on overall system performance. By expanding storage capacity without replacing hardware components, businesses can maintain optimal performance levels while accommodating increasing data demands. This translates into smoother operations, faster access times, and enhanced productivity for users.
Another advantage of scalable NAND Flash is its compatibility with various devices and architectures. Whether it’s servers, data centers, or personal computing devices like laptops or smartphones, NAND Flash can seamlessly integrate into different environments without requiring major modifications or complex configurations. This versatility makes it an ideal choice for organizations of all sizes and industries.
In summary, the scalability feature of NAND Flash empowers companies to meet their expanding storage needs effortlessly and efficiently. By allowing easy integration of additional modules without replacing existing hardware or reconfiguring architectures, businesses can scale up their storage capacity while maintaining performance and cost-effectiveness. As the demand for data storage continues to surge, NAND Flash’s scalability ensures that organizations can adapt and thrive in a rapidly evolving digital landscape.
High Cost
High Cost: A Drawback of NAND Flash Memory
NAND flash memory, with all its advantages and widespread usage, does have a downside: its relatively high cost compared to other types of memory, such as DRAM (Dynamic Random Access Memory) and SRAM (Static Random Access Memory).
The higher cost of NAND flash stems from several factors. Firstly, the manufacturing process for NAND flash memory is more complex and intricate than that of other memory types. It involves multiple layers of cells and intricate circuitry, which adds to the production costs.
Secondly, the materials used in NAND flash production, such as silicon wafers and specialized chemicals, contribute to the higher cost. These materials are essential for achieving the desired performance and reliability levels but come at a price.
Additionally, the demand for NAND flash memory has been consistently high due to its extensive use in various devices like smartphones, tablets, SSDs, and memory cards. This high demand further drives up prices as manufacturers need to balance supply with market needs.
However, it is important to note that while NAND flash may be more expensive than other memory types on a per-unit basis, it offers distinct advantages in terms of storage capacity and non-volatility. The higher cost is often justified by the benefits it brings to consumers who require large storage capacities or need data retention even when power is lost.
Over time, advancements in technology and economies of scale have helped reduce the cost of NAND flash memory. Manufacturers have been able to improve production efficiency and increase yields, leading to price reductions. As a result, we have seen a gradual decline in the cost per gigabyte of NAND flash over the years.
Furthermore, alternative technologies like 3D XPoint are emerging as potential competitors to NAND flash memory. These new technologies aim to bridge the gap between traditional storage solutions like DRAM and non-volatile memories like NAND flash by offering higher performance at lower costs. However, they are still in the early stages of development and adoption.
In conclusion, while the high cost of NAND flash memory can be seen as a drawback, it is important to consider the trade-offs and benefits it offers. The ongoing advancements in technology and increasing market competition will likely continue to drive down costs, making NAND flash more accessible to a wider range of applications in the future.
Limited Write Cycles
Limited Write Cycles: A Drawback of NAND Flash Technology
NAND Flash memory has undoubtedly revolutionized data storage with its numerous advantages. However, like any technology, it also has its limitations. One significant drawback of NAND Flash is its limited write cycles.
Every time data is written to a NAND Flash memory cell, it undergoes a process called program/erase (P/E) cycle. Over time, as the P/E cycles accumulate, the reliability of the memory cell diminishes. This means that after a certain number of write cycles, the cell may become less accurate in storing and retrieving data.
The limited write cycles of NAND Flash can be attributed to the physical characteristics of the technology itself. Each memory cell consists of a floating gate structure that traps electrical charges to represent binary data. However, during each write operation, these charges gradually leak away, causing the stored information to degrade over time.
Manufacturers have implemented various techniques to mitigate this limitation. One common approach is wear leveling, which distributes write operations evenly across different cells to ensure uniform wear and prolong overall lifespan. Additionally, error correction codes (ECC) are used to detect and correct any errors that may occur during read or write operations.
It’s important to note that different types of NAND Flash have varying endurance levels. SLC (Single-Level Cell) NAND offers higher endurance compared to MLC (Multi-Level Cell) and TLC (Triple-Level Cell) variants. SLC can endure hundreds of thousands or even millions of write cycles before experiencing reliability issues. On the other hand, MLC and TLC have higher storage densities but lower endurance levels.
Despite these mitigation techniques and advancements in technology, it’s crucial for users to be aware of the limited write cycles when utilizing NAND Flash-based devices. Heavy usage scenarios such as constant writes or running intensive applications may accelerate wear on certain cells and shorten their lifespan.
To maximize the longevity of NAND Flash-based devices, users can adopt practices such as minimizing unnecessary writes, optimizing storage usage, and regularly backing up important data. By understanding the limitations and implementing proper maintenance, users can make the most out of their NAND Flash-based storage solutions.
While limited write cycles are indeed a con of NAND Flash technology, it’s essential to consider them in the context of the numerous benefits it offers. The high-density storage, fast read/write speeds, durability, and energy efficiency make NAND Flash an indispensable component in various devices. As technology advances, manufacturers continue to explore ways to enhance endurance and reliability while maintaining the advantages of this groundbreaking storage solution.
Low Data Transfer Rates
Low Data Transfer Rates: A Trade-Off of NAND Flash
While NAND Flash has revolutionized data storage with its numerous advantages, it is not without its limitations. One significant drawback of NAND Flash technology is its relatively low data transfer rates compared to other memory types like DRAM (Dynamic Random Access Memory) and SRAM (Static Random Access Memory).
Data transfer rate refers to the speed at which data can be read from or written to a memory device. It plays a crucial role in determining the overall performance of storage systems. In this aspect, NAND Flash falls behind the faster access times provided by DRAM and SRAM.
The lower data transfer rates of NAND Flash can be attributed to the underlying architecture and operation principles of this type of memory. Unlike DRAM and SRAM, which are designed for high-speed data access, NAND Flash operates on a different principle that prioritizes density and cost-effectiveness.
NAND Flash memory cells are organized in a grid-like structure called a “memory array.” Each cell stores multiple bits of information, allowing for high-density storage. However, accessing individual cells within this array takes more time due to the need for additional operations like block erasing and programming.
Furthermore, NAND Flash utilizes a technique called “sequential access” rather than “random access” used by DRAM and SRAM. Sequential access means that data must be read or written in a sequential manner, which can result in slower overall transfer rates when dealing with fragmented or scattered data.
Despite these drawbacks, it is important to note that NAND Flash’s low data transfer rates are often outweighed by its other advantages such as high-density storage capabilities, durability, energy efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. While it may not excel in terms of raw speed, NAND Flash still offers satisfactory performance for most applications.
Moreover, advancements in NAND Flash technology have brought about improvements in transfer rates over time. Techniques such as multi-channel architectures and advanced error correction algorithms have been implemented to enhance data transfer speeds. Manufacturers are constantly working towards optimizing NAND Flash performance to bridge the gap with other memory types.
In conclusion, while NAND Flash may have lower data transfer rates compared to DRAM and SRAM, it remains a viable and widely used storage solution. Its advantages in terms of density, durability, energy efficiency, and cost-effectiveness often outweigh the trade-off in speed. As technology continues to progress, we can expect further enhancements in NAND Flash transfer rates, ensuring its continued relevance in the ever-evolving world of data storage.
Vulnerable to Power Loss
Vulnerable to Power Loss: Safeguarding Your Data
NAND Flash memory has undoubtedly revolutionized data storage with its numerous advantages. However, like any technology, it also has its limitations. One significant drawback of NAND Flash is its vulnerability to power loss during write operations, which can result in data corruption or even complete data loss.
When a write operation is in progress and power is suddenly lost, the process is abruptly interrupted. This can cause the incomplete data to be stored in an inconsistent state within the NAND Flash memory cells. As a result, the integrity of the stored information may be compromised.
To mitigate this risk and ensure data reliability, various techniques have been developed. One commonly used method is implementing error correction codes (ECC) within NAND Flash controllers. ECC algorithms help detect and correct errors that may occur during read or write operations. By adding redundancy to the stored data, ECC algorithms can reconstruct missing or corrupted bits, thereby minimizing potential damage caused by power loss.
Another approach involves using backup power sources such as supercapacitors or batteries in conjunction with NAND Flash devices. These backup power solutions provide temporary energy supply during unexpected power interruptions. They allow ongoing write operations to be completed or provide sufficient time for the system to save critical data before shutting down safely.
Additionally, some operating systems and file systems employ journaling techniques to protect against data loss due to sudden power failure. Journaling involves maintaining a log of all changes made before committing them permanently to NAND Flash memory. In case of a power loss event, the system can recover by replaying the journal and restoring the file system to its previous consistent state.
While these measures significantly reduce the risk of data corruption or loss caused by power failures, it’s important for users to also take precautions on their end. Regularly backing up critical data and maintaining reliable uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) can further safeguard against unexpected outages and minimize potential risks associated with power loss.
In conclusion, while NAND Flash memory offers numerous benefits, it is important to be aware of its vulnerability to power loss during write operations. By implementing error correction codes, utilizing backup power solutions, and employing journaling techniques, manufacturers and users can mitigate the risks associated with data corruption or loss. By taking these precautions and being mindful of potential power interruptions, we can ensure that our valuable data remains secure even in the face of unforeseen circumstances.
Tags: access times, battery life, boot-up times, cameras, compact, data centers, data storage, digital age, energy efficiency, energy-efficient, fast, fast read and write speeds, file transfers, gaming consoles, high-density storage capabilities, laptops, mechanical failures, memory cards, mobile devices, moving parts, multi-level cell ml, nand flash, nand flash memory, non-volatile storage technology, overall performance durability and reliability, program/erase cycles, reliable, revolutionizing data storage, shock, single-level cell slc, sleek designs, smartphones, solid-state drives ssds, solid-state nature, spinning magnetic disks, temperature variations, traditional hard disk drives hdds, types of nand flash, usb drives, vibration